导航
1前言
7后记
1 前言
RPC全称Remote Procedure Call(远程过程调用),它能让调用远端的函数就像调用本地函数一样容易。gRPC就是Google开发的RPC,软件巨头们几乎都开发过RPC框架,像微软的.Net Remoting、WCF,Fackbook的Thrift,阿里的Dubbo以及互联网兴起时的WebService等。但从性能、适用范围、流行程度多个维度来看,截止发文时止,gRPC目前全面领先于其它框架。

gRPC 使用语言中立的 Protocol Buffers 作为IDL(Interface Definition Language,接口定义语言),然后根据IDL自动生成服务端与客户端的代码。对开发人员来说,只需要使用Protocol Buffers定义函数以及函数使用的数据,gRPC自动生成服务端写客户端的代码,并完成通信(基于HTTP/2)的技术细节,使得开发人员可以把精力聚集于业务。
Protocol Buffers类似于JSON,是一种平台中立、语言中立的数据描述语言,它序列化传输效率比JSON更高。来源:https://www.wubayue.com
2 编译运行于Windows平台的gRPC
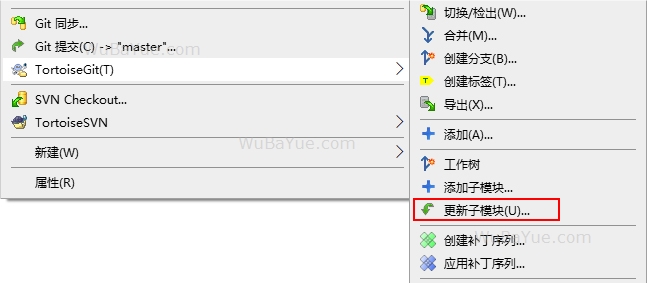
使用Git拉取源代码
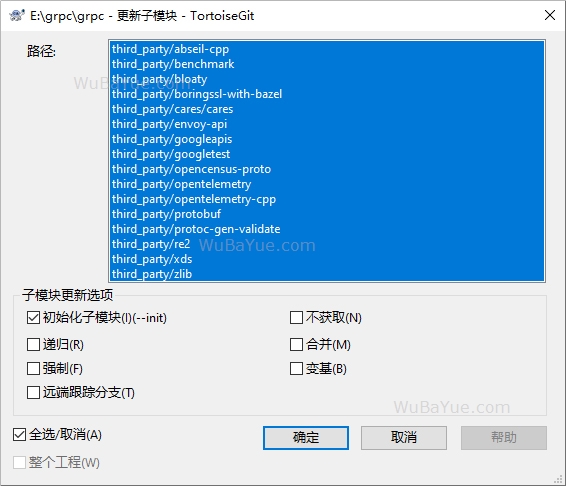
从 Git官方仓库 克隆gRPC的源代码,然后更新子模块,因为gRPC依赖了较多的三方库,这个过程会比较慢:
安装Go
在Go语言官网下载对应的Windows版本安装包,并完成安装:https://golang.google.cn/
安装Strawberry Perl
在Strawberry Perl官网下载对应的Windows版本安装包,并完成安装:https://strawberryperl.com/
安装NASM
在NASM官网下载对应的Windows版本安装包,并完成安装(将NASM安装路径配置在系统变量Path中):https://www.nasm.us/
安装CMake
在CMake官网下载对应的Windows版本安装包,并完成安装:https://cmake.org/
编译
在根目录中创建.build子目录,并在.build中执行cmake命令生成Visual Studio解决方案:
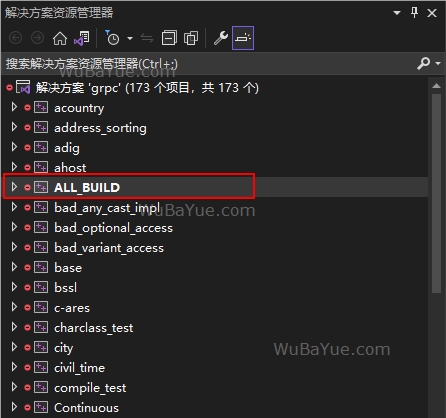
cmake .. -G "Visual Studio 17 2022" -A x64/Win32 -DgRPC_INSTALL=ON 使用管理员权限运行Visual Studio,打开grpc解决方案,编译 ALL_BUILD 项目(耗时较长):
解决“无法打开包括文件stdalign.h”的错误(可能出现):
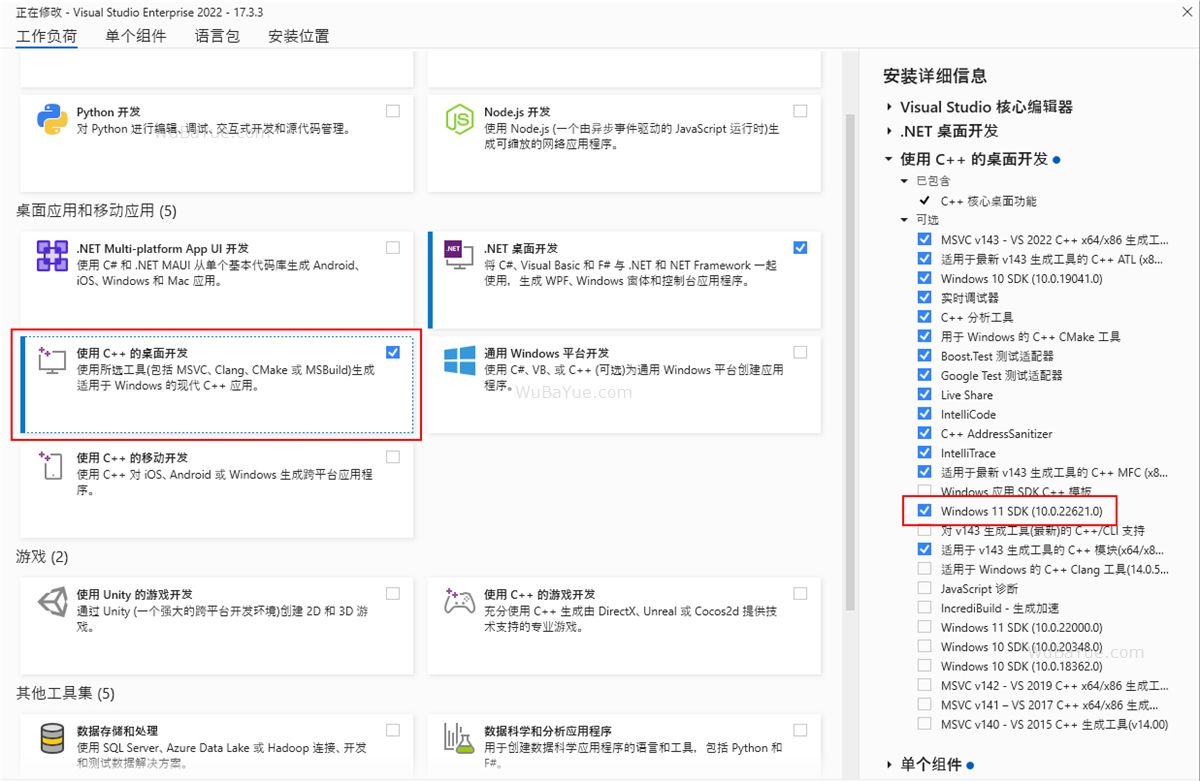
如果处于离线环境,也可以手动下载安装 最新的Windows SDK ,然后批量将项目的Windows SDK版本设置为新的版本号:
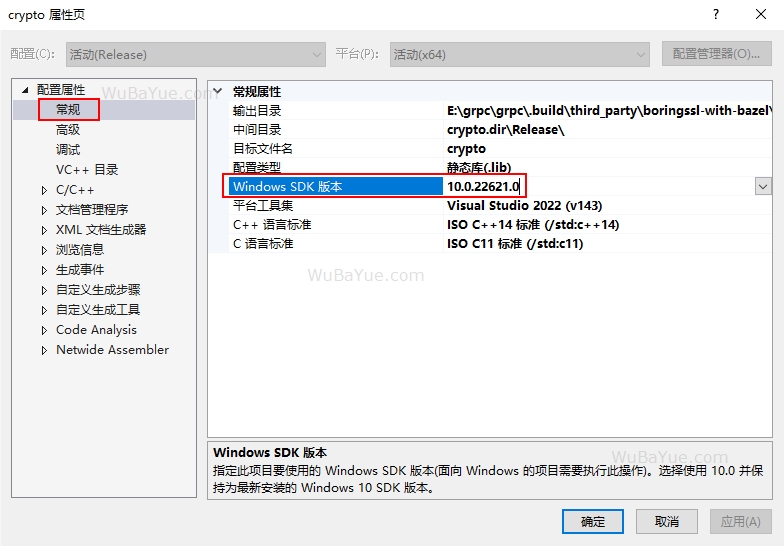
解决如下代码编译出错的问题(可能出现):
const float kUpb_FltInfinity = INFINITY;
const double kUpb_Infinity = INFINITY;
const double kUpb_NaN = NAN; 替换为:
const float kUpb_FltInfinity = (float)(1.0 / 0.0);
const double kUpb_Infinity = 1.0 / 0.0;
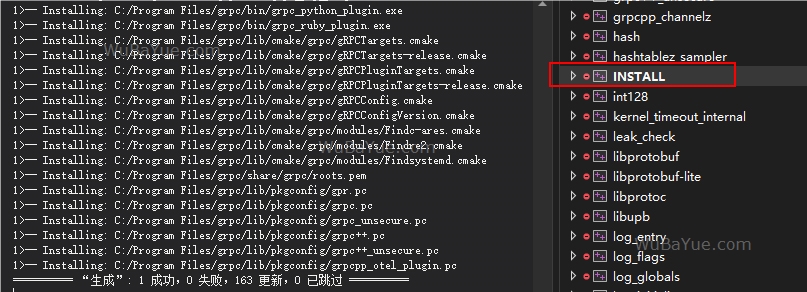
const double kUpb_NaN = 0.0 / 0.0; 安装
编译 INSTALL 项目进行安装,编译成功后gRPC默认安装在C:/Program Files/grpc目录中:来源:https://www.wubayue.com
3 Protocol Buffers介绍
Protocol Buffers数据类型
| 数据类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| bool | 布尔类型 |
| string | 字符串类型,支持UTF-8或ASCII文本,最大长度不能超过232。 |
| bytes | 字节流,最大长度不超过232。 |
| float | 单精度浮点类型 |
| double | 双精度浮点类型 |
| int32 | 32位整型,使用可变长度编码,如果包含负数建议使用sint32以提升效率。 |
| int64 | 64位整型,使用可变长度编码,如果包含负数建议使用sint64以提升效率。 |
| uint32 | 无符号32位整型,使用可变长度编码。 |
| uint64 | 无符号64位整型,使用可变长度编码。 |
| sint32 | 有符号32位整型,使用可变长度编码,在编码负数时比int32效率更高。 |
| sint64 | 有符号64位整型,使用可变长度编码,在编码负数时比int64效率更高。 |
| fixed32 | 无符号32位整型,使用固定4字节长度编码,如果值大于228,则效率高于uint32。 |
| fixed64 | 无符号64位整型,使用固定8字节长度编码,如果值大于256,则效率高于uint64。 |
| sfixed32 | 有符号32位整型,使用4字节固定长度编码。 |
| sfixed64 | 有符号64位整型,使用8字节固定长度编码。 |
Protocol Buffers中的枚举
enum Colors {
COLOR_UNKNOW = 0;
COLOR_RED = 1;
COLOR_BLUE = 2;
COLOR_GREEN = 3;
} 枚举中第一个项的值必须为0。来源:https://www.wubayue.com
Protocol Buffers中的结构体
message Person {
string Name = 1;
int Sex = 2;
int Ages = 3;
}4 编写proto文件
proto文件作为服务端与客户端的中间契约,在proto文件中定义函数、枚举、结构体等,然后根据proto文件自动生成不同语言的服务端与客户端代码。
在项目中创建一个Protobuf文件夹,用于存放编写的的proto文件,然后拷贝 gRPC安装目录/include/google/ 文件夹到创建的Protobuf目录中,google文件夹中包含了一些通过的.proto文件在我们编写.proto时需要用到,比如对基础数据类型的封装等。
将 gRPC安装目录/bin/ 文件夹中的protoc.exe、grpc_cpp_plugin.exe、grpc_csharp_plugin.exe三个文件拷贝至GrpcProtobuf文件夹中。它们用于将proto文件生成目标编程语言的源代码。
到此为止,准备工作就绪,参照 原始业务代码 编写proto文件如下:来源:https://www.wubayue.com
// 指定版本
syntax = "proto3";
// 引用公共的数据类型
import "google/protobuf/empty.proto";
import "google/protobuf/wrappers.proto";
// 命名空间
package GrpcDemo;
// 性别
enum Sex_Grpc {
SEX_UNKNOW_Grpc = 0;
SEX_MALE_Grpc = 1;
SEX_FEMALE_Grpc = 2;
}
// 课程
message Course_Grpc {
int32 courseID = 1;
string name = 2;
}
// 教师
message Teacher_Grpc {
int32 teacherID = 1;
string name = 2;
Sex_Grpc sex = 3;
Course_Grpc course = 4;
}
// 学生
message Student_Grpc {
int32 studentID = 1;
string name = 2;
Sex_Grpc sex = 3;
Teacher_Grpc teacher = 4;
repeated Course_Grpc courses = 5;
}
// 根据课程ID获取课程信息响应
message getCourse_Response {
Course_Grpc course = 1;
}
// 根据教师ID获取教师信息响应
message getTeacher_Response {
Teacher_Grpc teacher = 1;
}
// 获取开设的所有课程信息响应
message getStudents_Response {
repeated Student_Grpc students = 1;
}
service School_Grpc {
// 根据课程ID获取课程信息
rpc getCourse(google.protobuf.UInt32Value) returns (getCourse_Response) {}
// 根据教师ID获取教师信息
rpc getTeacher(google.protobuf.UInt32Value) returns (getTeacher_Response) {}
// 获取所有学生信息
rpc getStudents(google.protobuf.Empty) returns (getStudents_Response) {}
} 5 C++服务端
生成gRPC框架代码
protoc --proto_path=./ --cpp_out=./gen_cpp --grpc_out=./gen_cpp --plugin=protoc-gen-grpc=./grpc_cpp_plugin.exe School_Grpc.proto将生成的 School_Grpc.pb.h、School_Grpc.pb.cc、School_Grpc.grpc.pb.h、School_Grpc.grpc.pb.cc 四个文件拷贝至项目中。
项目配置
将 gRPC安装目录/bin/ 文件夹中的 zlib.dll 文件拷贝至项目编译输出目录,在项目编译过程中需要使用该文件。
在“项目属性 > C/C++ > 常规 > 附加包含目录”中增加 gRPC安装目录/include/
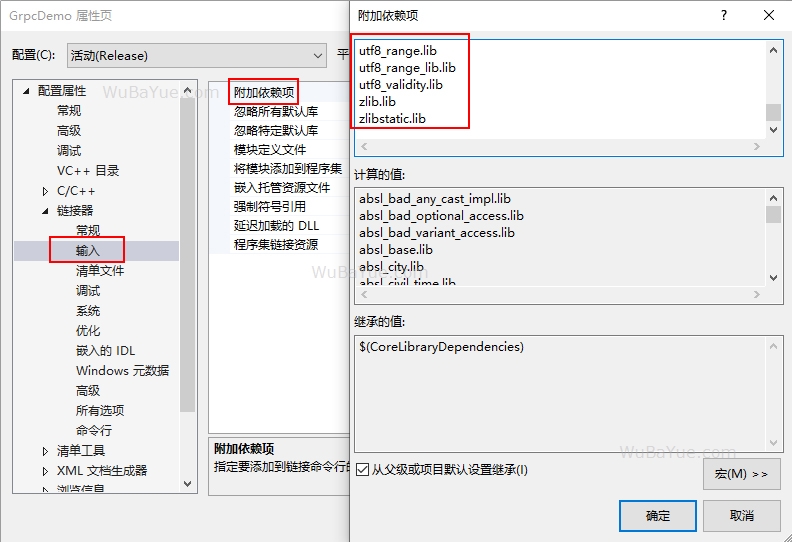
在“项目属性 > 链接器 > 常规 > 附加库目录”中增加 gRPC安装目录/lib/ ;在“项目属性 > 链接器 > 输入 > 附加依赖项”中将所有.lib文件配置进来。因文件较多,可使用“dir *.lib /b > libs.txt”命令将所有文件名写入文本文件,然后再拷贝至配置中:
原始业务代码
原始业务代码中简单描述了一所学校中老师、学生与课程之间的关系( School_Grpc.proto 中定义的内容与业务代码相一致),School.h:
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
namespace GrpcServer
{
// 性别
enum class Sex
{
SEX_MALE = 1,
SEX_FEMALE = 2
};
// 课程
typedef struct Course
{
// 课程ID
int courseID;
// 课程名称
std::string name;
Course() {}
Course(int courseID, const std::string& name)
{
this->courseID = courseID;
this->name = name;
}
} Course;
// 教师
typedef struct Teacher
{
// 教师ID
int teacherID;
// 教师姓名
std::string name;
// 教师性别
Sex sex;
// 主授课程
Course course;
Teacher() {}
Teacher(const int teacherID, const std::string& name, const Sex sex, const Course& course)
{
this->teacherID = teacherID;
this->name = name;
this->sex = sex;
this->course = course;
}
} Teacher;
// 学生
typedef struct Student
{
// 学生ID
int studentID;
// 学生姓名
std::string name;
// 学生性别
Sex sex;
// 导师
Teacher teacher;
// 选修课程
std::vector<Course> courses = {};
Student() {}
Student(const int studentID, const std::string& name, const Sex sex, const Teacher& teacher, const std::vector<Course>& courses)
{
this->studentID = studentID;
this->name = name;
this->sex = sex;
this->teacher = teacher;
this->courses.clear();
for (size_t i = 0; i < courses.size(); i++)
{
this->courses.push_back(courses[i]);
}
}
} Student;
// 学校
class School
{
public:
School();
~School();
// 根据课程ID获取课程信息
void getCourse(const int courseID, Course& course);
// 根据教师ID获取教师信息
void getTeacher(const int teacherID, Teacher& teacher);
// 获取所有学生信息
void getStudents(std::vector<Student>& students);
private:
std::vector<Course> _courses;
std::vector<Teacher> _teachers;
std::vector<Student> _students;
};
} School.cpp:
#include "School.h"
namespace GrpcServer
{
School::School()
{
// 课程初始化
this->_courses.clear();
this->_courses.push_back(Course(1, "Chinese"));
this->_courses.push_back(Course(2, "Mathematics"));
this->_courses.push_back(Course(3, "English"));
// 教师初始化
this->_teachers.clear();
Course course1;
this->getCourse(1, course1);
this->_teachers.push_back(Teacher(1, "Li Lei", Sex::SEX_MALE, course1));
Course course2;
this->getCourse(2, course1);
this->_teachers.push_back(Teacher(2, "Han Meimei", Sex::SEX_MALE, course2));
// 学生初始化
_students.clear();
// 导师
Teacher teacher;
this->getTeacher(1, teacher);
// 选修课程
std::vector<Course> courses;
Course course;
getCourse(1, course);
courses.push_back(course);
_students.push_back(Student(1, "Wu Ba Yue", Sex::SEX_MALE, teacher, courses));
}
School::~School()
{
this->_courses.clear();
this->_teachers.clear();
this->_students.clear();
}
void School::getCourse(const int courseID, Course& course)
{
if (courseID <= 0 || _courses.size() == 0)
return;
for (size_t i = 0; i < _courses.size(); i++)
{
if (courseID == _courses[i].courseID)
{
course.courseID = _courses[i].courseID;
course.name = _courses[i].name;
return;
}
}
}
void School::getTeacher(const int teacherID, Teacher& teacher)
{
if (teacherID <= 0 || _teachers.size() == 0)
return;
for (size_t i = 0; i < _teachers.size(); i++)
{
if (teacherID == _teachers[i].teacherID)
{
teacher.teacherID = _teachers[i].teacherID;
teacher.name = _teachers[i].name;
teacher.sex = _teachers[i].sex;
teacher.course = _teachers[i].course;
return;
}
}
}
void School::getStudents(std::vector<Student>& students)
{
students.clear();
for (size_t i = 0; i < _students.size(); i++)
{
students.push_back(_students[i]);
}
}
} Grpc服务结合业务逻辑
创建一个 SchoolGrpcService 类,让它承继自通过.proto自动生成的 School_Grpc::Service 类,然后通过重写 School_Grpc::Service 中的方法,将业务逻辑与Grpc服务相结合。SchoolGrpcService.h:
#pragma once
#include "School_Grpc.grpc.pb.h"
#include "School.h"
using grpc::Server;
using namespace google::protobuf;
using namespace GrpcDemo;
namespace GrpcServer
{
// 通过继承并重写 School_Grpc::Service 中的方法,将业务逻辑与Grpc服务相结合
class SchoolGrpcService final : public School_Grpc::Service
{
#pragma region 数据转换
public:
static Sex_Grpc Sex_ToGrpc(const Sex sex);
static Sex Sex_FromGrpc(const Sex_Grpc sex_Grpc);
static bool Course_ToGrpc(const Course& course, Course_Grpc& course_Grpc);
static bool Course_FromGrpc(const Course_Grpc& course_Grpc, Course& course);
static bool Teacher_ToGrpc(const Teacher& teacher, Teacher_Grpc& teacher_Grpc);
static bool Teacher_FromGrpc(const Teacher_Grpc& teacher_Grpc, Teacher& teacher);
static bool Student_ToGrpc(const Student& student, Student_Grpc& student_Grpc);
static bool Student_FromGrpc(const Student_Grpc& student_Grpc, Student& student);
#pragma endregion
#pragma region 构造与析构
private:
School* _school;
public:
SchoolGrpcService(School* school);
~SchoolGrpcService();
#pragma endregion
#pragma region 业务逻辑
public:
// 根据课程ID获取课程信息
::grpc::Status getCourse(::grpc::ServerContext* context, const ::google::protobuf::UInt32Value* request, ::GrpcDemo::getCourse_Response* response) override;
// 根据教师ID获取教师信息
::grpc::Status getTeacher(::grpc::ServerContext* context, const ::google::protobuf::UInt32Value* request, ::GrpcDemo::getTeacher_Response* response) override;
// 获取所有学生信息
::grpc::Status getStudents(::grpc::ServerContext* context, const ::google::protobuf::Empty* request, ::GrpcDemo::getStudents_Response* response) override;
#pragma endregion
};
} gRPC的应用场景通常是先有某些业务逻辑,然后使用gRPC将这些业务逻辑提供给外部调用,因此数据结构(枚举、结构体等)通常会存在两份,业务逻辑中的与.proto中的,两者之间需要进行转换,SchoolGrpcService.cpp:
#include "SchoolGrpcService.h"
namespace GrpcServer
{
#pragma region 数据转换
Sex_Grpc SchoolGrpcService::Sex_ToGrpc(const Sex sex)
{
switch (sex)
{
default:
case Sex::SEX_MALE:
return Sex_Grpc::SEX_MALE_Grpc;
case Sex::SEX_FEMALE:
return Sex_Grpc::SEX_FEMALE_Grpc;
}
}
Sex SchoolGrpcService::Sex_FromGrpc(const Sex_Grpc sex_Grpc)
{
switch (sex_Grpc)
{
default:
case Sex_Grpc::SEX_MALE_Grpc:
return Sex::SEX_MALE;
case Sex_Grpc::SEX_FEMALE_Grpc:
return Sex::SEX_FEMALE;
}
}
bool SchoolGrpcService::Course_ToGrpc(const Course& course, Course_Grpc& course_Grpc)
{
course_Grpc.set_courseid(course.courseID);
course_Grpc.set_name(course.name);
return true;
}
bool SchoolGrpcService::Course_FromGrpc(const Course_Grpc& course_Grpc, Course& course)
{
course.courseID = course_Grpc.courseid();
course.name = course_Grpc.name();
return true;
}
bool SchoolGrpcService::Teacher_ToGrpc(const Teacher& teacher, Teacher_Grpc& teacher_Grpc)
{
teacher_Grpc.set_teacherid(teacher.teacherID);
teacher_Grpc.set_name(teacher.name);
teacher_Grpc.set_sex(Sex_ToGrpc(teacher.sex));
// 结构体成员赋值方式
Course_Grpc course_Grpc;
Course_ToGrpc(teacher.course, course_Grpc);
teacher_Grpc.mutable_course()->CopyFrom(course_Grpc);
return true;
}
bool SchoolGrpcService::Teacher_FromGrpc(const Teacher_Grpc& teacher_Grpc, Teacher& teacher)
{
teacher.teacherID = teacher_Grpc.teacherid();
teacher.name = teacher_Grpc.name();
teacher.sex = Sex_FromGrpc(teacher_Grpc.sex());
Course_FromGrpc(teacher_Grpc.course(), teacher.course);
return true;
}
bool SchoolGrpcService::Student_ToGrpc(const Student& student, Student_Grpc& student_Grpc)
{
student_Grpc.set_studentid(student.studentID);
student_Grpc.set_name(student.name);
student_Grpc.set_sex(Sex_ToGrpc(student.sex));
// 结构体成员赋值方式
Teacher_Grpc teacher_Grpc;
Teacher_ToGrpc(student.teacher, teacher_Grpc);
student_Grpc.mutable_teacher()->CopyFrom(teacher_Grpc);
// vector成员赋值方式
student_Grpc.clear_courses();
if (student.courses.size() > 0)
{
std::vector<Course_Grpc> vecCourseGrpc;
for (size_t i = 0; i < student.courses.size(); i++)
{
Course_Grpc course_Grpc;
Course_ToGrpc(student.courses[i], course_Grpc);
vecCourseGrpc.push_back(course_Grpc);
}
student_Grpc.mutable_courses()->Add(vecCourseGrpc.begin(), vecCourseGrpc.end());
}
return true;
}
bool SchoolGrpcService::Student_FromGrpc(const Student_Grpc& student_Grpc, Student& student)
{
student.studentID = student_Grpc.studentid();
student.name = student_Grpc.name();
student.sex = Sex_FromGrpc(student_Grpc.sex());
Teacher_FromGrpc(student_Grpc.teacher(), student.teacher);
student.courses.clear();
for (size_t i = 0; i < student_Grpc.courses_size(); i++)
{
Course course;
Course_FromGrpc(student_Grpc.courses(i), course);
student.courses.push_back(course);
}
return true;
}
#pragma endregion
#pragma region 构造与析构
SchoolGrpcService::SchoolGrpcService(School* school)
{
this->_school = school;
}
SchoolGrpcService::~SchoolGrpcService()
{
if (this->_school != nullptr)
this->_school = nullptr;
}
#pragma endregion
#pragma region 业务逻辑
::grpc::Status SchoolGrpcService::getCourse(::grpc::ServerContext* context, const ::google::protobuf::UInt32Value* request, ::GrpcDemo::getCourse_Response* response)
{
if (this->_school != nullptr)
{
// 调用业务逻辑
Course course;
this->_school->getCourse(request->value(), course);
// 结果转换
Course_Grpc course_Grpc;
Course_ToGrpc(course, course_Grpc);
// 结果返回
response->mutable_course()->CopyFrom(course_Grpc);
}
return ::grpc::Status::OK;
}
::grpc::Status SchoolGrpcService::getTeacher(::grpc::ServerContext* context, const ::google::protobuf::UInt32Value* request, ::GrpcDemo::getTeacher_Response* response)
{
if (this->_school != nullptr)
{
// 调用业务逻辑
Teacher teacher;
this->_school->getTeacher(request->value(), teacher);
// 结果转换
Teacher_Grpc teacher_Grpc;
Teacher_ToGrpc(teacher, teacher_Grpc);
// 结果返回
response->mutable_teacher()->CopyFrom(teacher_Grpc);
}
return ::grpc::Status::OK;
}
::grpc::Status SchoolGrpcService::getStudents(::grpc::ServerContext* context, const ::google::protobuf::Empty* request, ::GrpcDemo::getStudents_Response* response)
{
if (this->_school != nullptr)
{
// 调用业务逻辑
std::vector<Student> students;
this->_school->getStudents(students);
// 结果转换
std::vector<Student_Grpc> vecStudentsGrpc;
if (students.size() > 0)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < students.size(); i++)
{
Student_Grpc student_Grpc;
Student_ToGrpc(students[i], student_Grpc);
vecStudentsGrpc.push_back(student_Grpc);
}
}
// 结果返回
response->clear_students();
if (vecStudentsGrpc.size() > 0)
response->mutable_students()->Add(vecStudentsGrpc.begin(), vecStudentsGrpc.end());
}
return ::grpc::Status::OK;
}
#pragma endregion
} 开启gRPC服务
gRPC服务在单独的线程中监听指定的端口,通过Http协议进行通信,GrpcService.h:
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <grpcpp/grpcpp.h>
#include <grpcpp/ext/proto_server_reflection_plugin.h>
#include <grpcpp/health_check_service_interface.h>
#include "SchoolGrpcService.h"
namespace GrpcServer
{
class GrpcService
{
public:
GrpcService();
~GrpcService();
// 启动Grpc服务
bool start();
private:
School* _pSchool;
SchoolGrpcService* _pSchoolGrpcService;
// gRPC服务线程相关
bool _isGrpcServiceStarted;
std::shared_ptr<std::thread> _pGrpcServiceThread;
void grpcServiceThread();
};
} GrpcService.cpp:来源:https://www.wubayue.com
#include "GrpcService.h";
namespace GrpcServer
{
GrpcService::GrpcService()
{
_pSchool = new School();
_pSchoolGrpcService = new SchoolGrpcService(_pSchool);
_isGrpcServiceStarted = false;
}
GrpcService::~GrpcService()
{
if (_pSchoolGrpcService != nullptr)
{
delete _pSchoolGrpcService;
_pSchoolGrpcService = nullptr;
}
if (_pSchool != nullptr)
{
delete _pSchool;
_pSchool = nullptr;
}
_isGrpcServiceStarted = false;
}
bool GrpcService::start()
{
if (_isGrpcServiceStarted)
return false;
// 在单独的线程中运行gRPC服务
_pGrpcServiceThread = std::make_shared<std::thread>(&GrpcService::grpcServiceThread, this);
_isGrpcServiceStarted = true;
return true;
}
void GrpcService::grpcServiceThread()
{
grpc::EnableDefaultHealthCheckService(true);
grpc::reflection::InitProtoReflectionServerBuilderPlugin();
grpc::ServerBuilder builder;
// 在所有IP段监听8888端口
builder.AddListeningPort("0.0.0.0:8888", grpc::InsecureServerCredentials());
builder.RegisterService(_pSchoolGrpcService);
std::unique_ptr<grpc::Server> server(builder.BuildAndStart());
server->Wait();
}
}
int main()
{
GrpcServer::GrpcService grpcService;
std::cout << "Grpc server start " << (grpcService.start() ? "succeed." : "failed.") << std::endl;
std::string k;
std::cin >> k;
return 0;
} 6 C++客户端
拷贝gRPC框架代码
将章节5中生成的 School_Grpc.pb.h、School_Grpc.pb.cc、School_Grpc.grpc.pb.h、School_Grpc.grpc.pb.cc 四个文件拷贝至项目中。
项目配置
客户端项目配置与服务端完全相同,将 gRPC安装目录/bin/ 文件夹中的 zlib.dll 文件拷贝至项目编译输出目录,在项目编译过程中需要使用该文件。
在“项目属性 > C/C++ > 常规 > 附加包含目录”中增加 gRPC安装目录/include/
在“项目属性 > 链接器 > 常规 > 附加库目录”中增加 gRPC安装目录/lib/ ;在“项目属性 > 链接器 > 输入 > 附加依赖项”中将所有.lib文件配置进来。
客户端代码
SchoolGrpcClient.h:
#pragma once
#include <grpcpp/grpcpp.h>
#include "School_Grpc.grpc.pb.h"
namespace GrpcClient
{
class SchoolGrpcClient
{
private:
std::unique_ptr<GrpcDemo::School_Grpc::Stub> _stub;
public:
SchoolGrpcClient(std::shared_ptr<grpc::Channel> channel);
GrpcDemo::School_Grpc::Stub* getStub();
};
} SchoolGrpcClient.cpp:来源:https://www.wubayue.com
#include "SchoolGrpcClient.h"
namespace GrpcClient
{
// 创建Stub对象(Stub可理解为服务端的代理)
SchoolGrpcClient::SchoolGrpcClient(std::shared_ptr<grpc::Channel> channel)
: _stub(GrpcDemo::School_Grpc::NewStub(channel)) {
}
// 对外提供Stub对象
GrpcDemo::School_Grpc::Stub* SchoolGrpcClient::getStub()
{
return _stub.get();
}
}
int main()
{
auto channel = grpc::CreateChannel("127.0.0.1:8888", grpc::InsecureChannelCredentials());
GrpcClient::SchoolGrpcClient client(channel);
grpc::ClientContext context;
google::protobuf::Empty request;
GrpcDemo::getStudents_Response response;
// 获取Stub对象,调用服务端:获取所有学生信息
grpc::Status status = client.getStub()->getStudents(&context, request, &response);
if (status.ok())
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < response.students_size(); i++)
{
std::cout << "studentID : " << response.students(i).studentid() << std::endl;
std::cout << "name : " << response.students(i).name() << std::endl;
}
}
} 7 后记
本文详细描述了gRPC在C++环境中的编译安装,展示了如何通过Protocol Buffers编写一个gRPC服务并生成源代码,然后通过代码示例了gRPC的C++服务端与客户端。计划还会补充一篇《gRPC进阶:通过流模式实现观察者模式》,用来说明事件(信号槽)在gRPC中的应用示例,这样对gRPC的介绍就基本完整了。来源:https://www.wubayue.com
<全文完>